Cells are the fundamental units of life, and all living organisms are made of cells.
These cells are of different types based on their structure, function, and role in the body’s physiology.
Though all the cells have their internal physiology, there are many differences among them.
The differences are based on evolution periods, adaptability, and requirements for living.
Here, we discuss broadly different cells in living beings.
You can also read the types of cells in the human body alone.
Types of cells
- Prokaryotic cells:
- Eukaryotic cells
- Cancer cells
- Stem cells
- Animal cells
- Plant cells
Prokaryotic cells
These cells are present only in a few microorganisms like bacteria and a few algae. They are considered as a primitive type of cells.
The name prokaryotic is due to the absence of well-defined nuclei in them. The nuclear material like the DNA and other essentials are present in the cytoplasm itself along with other regular cell organelles.
The process of transcription and translation co-occur as there is no need for mRNA to travel out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
They have 70S ribosomes which have two subunits as 30S and 50S sub-unit.
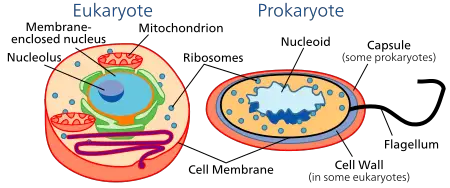
Eukaryotic cells:
These cells are highly evolved cells and are considered to be more advanced forms than prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells have a distinct nucleus within them. The nucleus hosts DNA, nucleolus and other essentials within. The process of transcription occurs inside the nucleus. The mRNA formed inside the nucleus due to transcription comes out into the cytoplasm and is involved in the translation process. These cells have 80S ribosomes, which have two subunits, 40S and 60S.
Almost all plants and animals have eukaryotic cells. See the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Cancer cells:
These cells are normal animal cells but with disturbed physiology and structure.
These cells grow faster than others and are also bigger in size. Further, they do not have death, unlike normal cells.
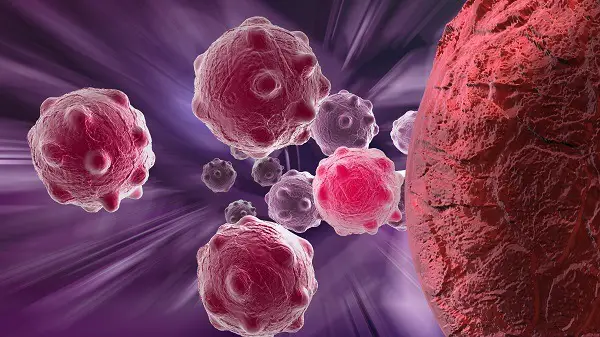
So they tend to keep on growing. Normal cells enhance the life of the organism, while these cells lead to the death of the organism.
Stem cells:
These are the cells that are formed in animals especially and can differentiate into any required body cell.
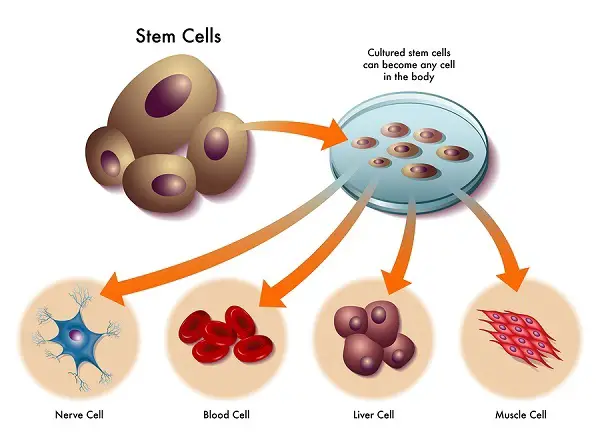
These cells can be obtained from the bone marrow in adults and from the umbilical cord in children.
The ability of these cells to convert into other cells is called as totipotency.
Animal cells:
These cells are eukaryotic cells and are present in animals.
They are of different types and vary from animal to animal. These cells are quite different from plant cells regarding food procurement, waste treatment, metabolism, etc.
These cells work in mutual harmony, and they form many different tissues and organs to carry out various functions within the body.
They are susceptible to contract diseases and also repair themselves. They are divided by processes like mitosis and meiosis.
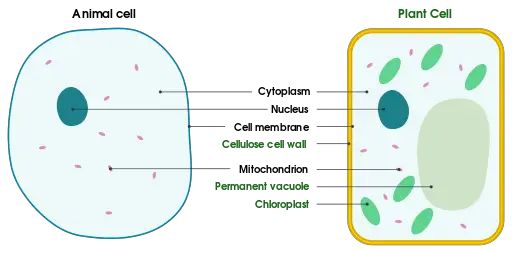
Plant cells:
These cells are present within the plants. They are of few types, and unlike animal cells, they are very few different varieties.
They lose their internal function gradually over age and are either shed off the plant or located within it to give structural strength to the plant.
With growth in age, the cells are deposited by various phytochemicals like chitin lignin, which make them hard and thick.