Human Anatomy and physiology are interlinked subjects in the study of medicine.
One is not complete without the study of another.
They are completely interrelated systems in the body. But one is related to structure, and the other is related to function.
- Anatomy deals with structure from minute levels to macro levels.
- Similarly, physiology also exists from minute levels to macro levels.
- Though they are different, one must study them as human anatomy and physiology to understand how they combine to make up a living person.
However, understanding the differences and similarities will help us grasp the subject better.
Anatomy vs. Physiology comparison
| Feature/Role | Anatomy | Physiology |
|---|---|---|
| Concerned with | The structure and appearance | The functions, activities, performance and efficiency |
| Can be Studied | Individually and specifically, such as the heart anatomy, liver anatomy, lung anatomy, etc. | It can be studied individually but is incomplete without connecting with other’s physiology. |
| Depth of study | Anatomy appears simple and limited, but it is very complex to study. | Physiology appears complex, but it is simple and a limited study |
| Range of study | Reflex actions, homeostasis, pain, protection, and other regulation. | Physiology also extends from micro to macro, but the details are so specific and limited. |
| Role and safeguards by | It is protected through a bone cage (skull) for the brain and a thorax for the heart. Wear and tear resistance by keratinized skin and adipose tissue. | The functions, activities, performance, and efficiency |
| Diseases | Fewer diseases due to only anatomical derangement | Major diseases are due to physiological derangements. For example, diabetes and hypertension. |
| Injuries | Physical injury causes damage to anatomy. | Both Physical and mental (emotional) injuries cause damage to the physiology. |
| Explanation/demonstration | By specimens, histology, size, shape, etc. | By biochemical analysis, pulse measurements, blood pressure, etc. |
| Replacement/substitutes | Anatomical damages, to some extent, can be managed without death | Physiological damage would lead to death and rarely be replaced. |
| The repair can be done by | Cellular, tissue, or organ replacement | The repair can be done only by substituents like nutrition, vitamins, hormones, enzymes, etc. |
| For student | Anatomy is hard to remember and study due to scientific words that need memory. | Physiology is easier to study and remember when combined with anatomy. |
1. Anatomy is more about the body’s structure, appearance, shape, and organization.
- It describes the cell, cell structure, and cell organelles. There are many types of anatomy.
- Further, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole body.
- On the other hand, physiology describes the functioning and mechanism of the above-mentioned structures in detail.
- It also describes their ultimate contrition to the living organism.
2. Each organ or structure can be studied individually.
- In a cell, we can study the structure of the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc.
- In the organ, we can study the structure of tissues, their arrangements, etc.
- In the whole body, we will describe the arrangement of various organs at different locations and their connections with other systems.
- Eventually, we will be detailed about each and every element with reference to shape, size, color, texture, location, etc.
- But, for physiology, this becomes simplified as to what specific function these anatomical entities play.
Overall, how they would relate to each other towards one specific goal, i.e., life.
3. The anatomy looks simple, limited, and easier. But, it is very vast and complex and takes a long time to study.
- It is even harder to remember the structures unless one knows the diagram.
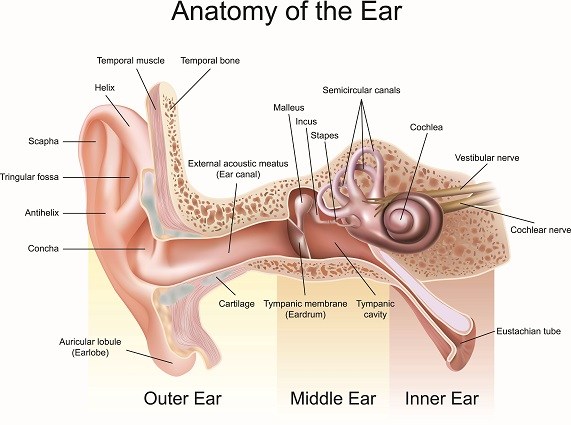
- However, physiology, though it appears complex, is very specific and limited in detail. One could easily remember physiology more than anatomy.
- In the above ear anatomy diagram, there are many anatomical parts.
- However, there are only two physiological functions.
- One is for hearing and conducting sound to the body.
- The other function is giving balance to the body.
But, by structure, it looks very complex.
4. The anatomy of the is not always disturbed by diseases.
- But almost all diseases affect physiology.
- So, to be healthy, physiology should be intact, which is supported by homeostasis.
5. Physical injuries lead to damage to body parts.
- In comparison, physiology is damaged mostly by mental trauma and stress.
6. Anatomical damages always do not lead to death.
- But most of the physiological damages could lead to death.
7. Anatomy repairs are done by replacement and surgical procedures.
- However, disturbed physiology is repaired by supplements like nutrition, vitamins, hormones, enzymes, etc.
8. Anatomy is assessed by shape, size, color, microscopy, etc.
- Physiology is assessed by rate (like heart rate), biochemical changes in the body fluids, etc.
9. Bony framework, skin, and reflex actions prevent damage to anatomy.
In contrast, homeostasis and feedback mechanisms prevent damage to body physiology.