Human Cells are of different types based on their structure and function.
A Cell is the basic unit of life, and a group of them forms tissues, and further, a group of tissues forms an organ.
Thus, human cells are designed by nature to meet the end anatomy and physiological requirements.
Different Types of Human Cells by Structure
Structurally, Cells are of various kinds, like
1. Bone cells
- These cells, unlike others, are the hardest of the body cells.
- The presence of calcium and phosphate material binds them together.
- They provide structural shape, strength, and movement to the body.
- Forming bone cages, they help enclose and protect essential organs like the brain, heart, lungs, eyes, etc.
2. Cartilage cells (Chondrocytes)
- These cells are part of the cartilage bones in the body.
- They are similar to bone cells, but they form flexible elastic tissue due to the binding material.
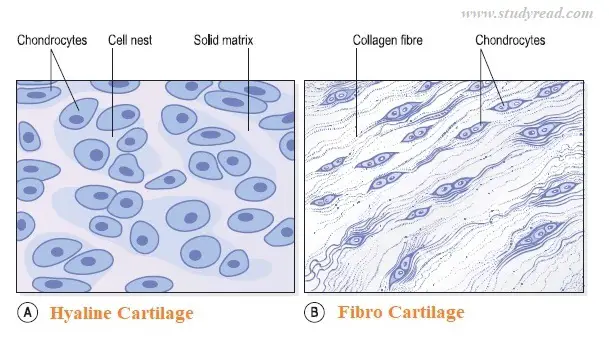
- The matrix around these chondrocyte cells is loose and flexible compared to those of bone cells.
- Hence, the cartilage tissue can be freely bent, as in the external ear.
- They form the ear pinna, knee caps, and intervertebral discs and are also present in between large bones to help them move freely, like in between two ribs, spinal bones, and joints.
3. Nerve cells
- These cells are part of the nervous system.
- Some of these cells are the longest cells of the body, ranging up to 100 centimeters in length.
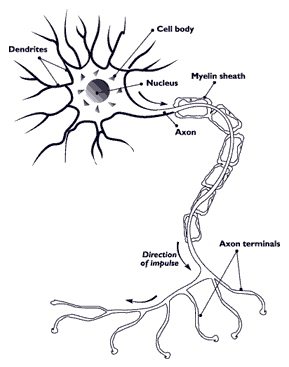
- Structurally, they are long, with many branches at either end.
- Unlike other cells, they never undergo cell division or multiply during their lifetime.
- Once formed during the fetus stage, they live until the entire life of an individual.
- They are present all over the body and extend to the superficial and deeper parts of the body.
- These cells are found in the brain and the spinal cord. They combine to form the nervous tissue.
4. Epithelial cells
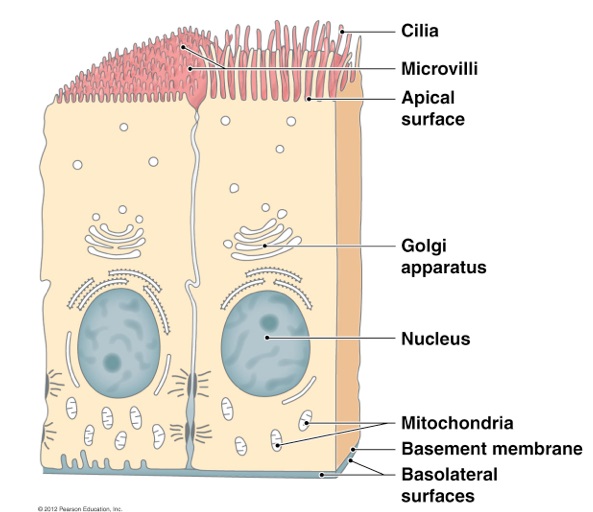
- These cells form surface-covering tissues.
- They are of different shapes and sizes, like cuboidal, flattened, columnar, etc.
- They can be found as covering layers for all the organs and as inner linings.
- They are present in the skin, scalp, respiratory tract, digestive tract, over the surface of the heart, and more.
- Ex: Skin cells, mucous cells.
- They also form essential structures, like the nephrons in the kidney, that help filter the blood.
5. Muscle cells
- These cells are responsible for the movements of the body.
- They are also called myocytes and are present in the muscle tissues.
- They are rich in proteins like actin and myosin, which are involved in the contraction and relaxation process.
- They are mostly long and large and can provide movements to the body.
- There are three types of muscle cells, viz., the skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle cells.
- Skeletal muscle cells are attached to long bones and assist in their movements (by muscle contraction).
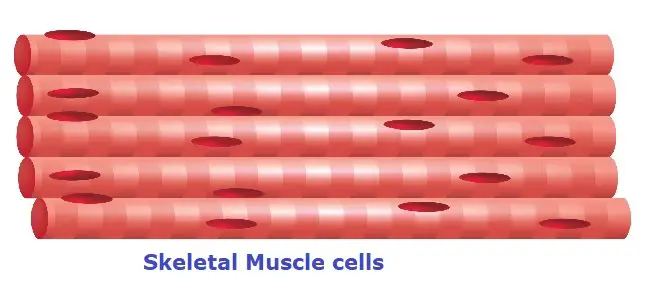
- They are also called striated cells as they have bands or striations on them, as seen above (white and red bands).
- These bands indicate actin and myosin filaments, which help in contraction.
- Cardiac muscle cells are present only in the heart muscle and responsible for heartbeats.
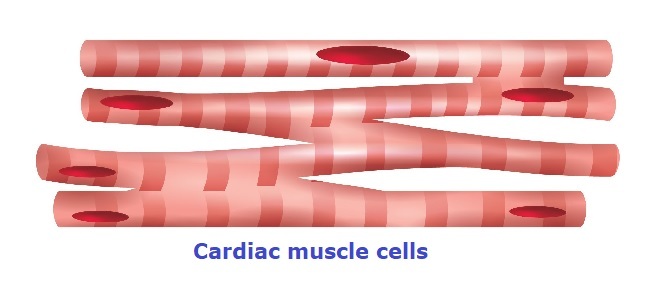
- These are also striated but have branches with others.
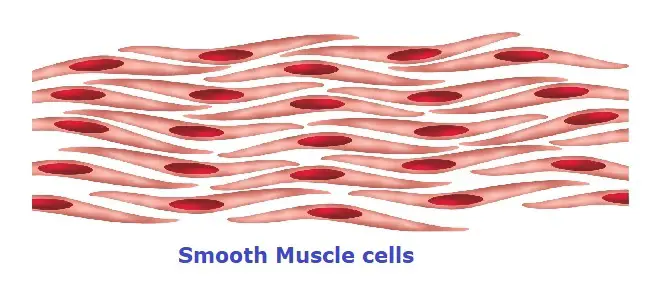
- Smooth muscle cells are flexible yet can contract and relax with ease.
- They are present in the stomach, intestine, and blood vessel walls (vascular tissue), helping move food through the gut.
- Muscle cells also store glucose, which generates the body’s energy and heat.
6 Secretory cells
- These cells, as the name indicates, are secretory in function.
- Their size is comparatively large and mostly present in the glands.
- They secrete specific secretions containing enzymes or hormones.
Examples:
a) Salivary gland cells called acini secrete saliva
b) Gastric cells present in the stomach secrete gastric juice.
7. Adipose cells
- Fat cells are spread in a loose areolar matrix to form adipose tissue.
- Adipocytes are large and filled with large fat globules, which causes the nucleus to be pushed to one side.

- These adipose tissue cells are mainly seen in the soles, palms, and bums below the skin.
Their main function is
- To store energy (as fat)
- Prevent heat loss from the skin.
- Maintain body temperature,
- Reduce friction due to contact with hard surfaces.
8. Blood cells

These cells include three basic types, like
a) Red blood cells (RBCs):
- These cells are called corpuscles and are not living in nature due to the absence of a nucleus in them.
- They are red-colored due to the presence of pigment hemoglobin. Their primary role is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
b) White blood cells (WBCs):
- Unlike RBCs, they have a nucleus and are living.
- They are of five different types and play a prominent role in body defense against pathogens.
c) Thrombocytes (platelets).
- These cells are the small of the three and are involved in the process of hemostasis, i.e., blood clot formation, to prevent bleeding due to injury.
- These cells are always motile and never stay in one place. They have a limited lifespan before they are destroyed in the body.
- Unlike other cells, they never multiply to form new cells. Instead, new cells are formed from other cells.
Cell types based on their function
Different cells carry out distinct functions in the body, like
Conductive cells
- Nerve cells and muscle cells come under this category.
- They have an inherent ability to conduct an electric impulse from one region to other distant body areas.
Connective cells
- Bone cells and blood cells come under this category.
- They help connect other cells and tissues.
Glandular cells
- These cells are secretory in nature.
- They form glands like the pancreas, salivary glands, etc., and help produce enzymes, hormones, etc.
Storage cells
- Adipose cells, some liver cells, store materials like fat for later use.
- This fat is consumed in times of starvation and excess cold temperatures.
Supportive cells
- These are the cells that are present as support to adjacent cells.
Ex: The Glial cells present in the brain and spinal cord nourish the nerve cells and protect them from shocks and trauma.
The special type of cells
- These are specialized cells with some crucial functions. They are
a) Sperms
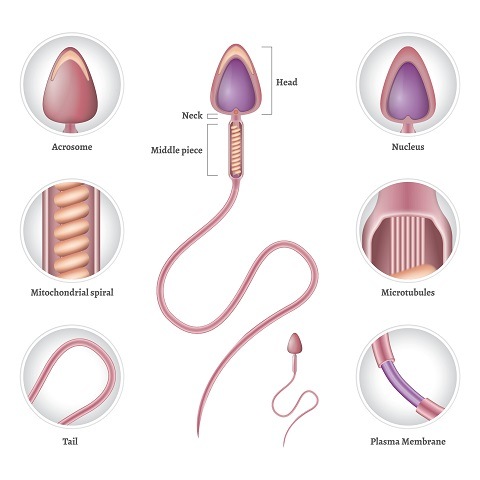
- These cells, unlike others, have haploid DNA with 23 chromosomes (i.e., have only one set of chromosomes).
- They are present only in males after puberty in the seminal vesicles.
- These cells have a tail that enables them to swim and move in the female uterus.
- They also release an enzyme hyaluronidase, which helps them penetrate through uterine tissue and reach the oocytes.
b) Oocytes
- Cells are haploid and present in the adult female genital system.
- They are also haploid, like the sperms.
- They start to form after puberty and continue so till the stage of menopause.
- They accept sperm cells to form a zygote (fertilized egg). This zygote further grows in the uterus to form a baby.
c) Stem cells
- These are parent cells that can differentiate into any other body cell when required.
- These stem cells have gained prominence due to their promising role in treating diseases.
d) Rods & cones of eyes
- These cells are present exclusively in the retina of the eye.
- They contain photosensitive pigments that help to capture the light and convert it into a nerve impulse.
e) Ciliated cells
- These cells are in the lining of the respiratory tract and esophagus and have threadlike cilia, which move in one direction.
- Their movement helps move food from the buccal cavity into the stomach and phlegm and other wastes out of the respiratory tract.
f) Blood cells
- These are quite interesting cells as they are freely moving in the body. Blood cells freely flow in the liquid blood.
- Some of them are not alive (RBCs), while others are alive and have varied shapes like WBCs and platelets (spindle shape).
- Further, these WBCs are of different types. Of them, macrophages can eat (gulp) any foreign particle like bacteria in the body. Hence, they are body defense cells.
g) Islets of the Pancreas
- These cells secrete pancreatic hormones like insulin and glucagon.
- There are a total of 5 types. Check out pancreatic cells for details.
h) Hepatocytes
- These cells are present in the liver and constitute 80% of its mass. They are involved in breaking down toxins like drugs and other waste materials.
- The cells are large with many mitochondria and abundant endoplasmic reticulum to help liver function.
- Unlike other body cells, they are the only ones that can regenerate.
i) Kupffer cells
- These cells are located in the liver and are modified macrophage cells.
- They destroy the old and worn-out red blood cells in the liver.
J) Goblet cells
- These cells are dispersed in the inner layer of the small intestine, and they secrete mucus.
K) Paneth cells
- Paneth cells are also found in intestinal linings.
- They secrete anti-microbial proteins and help defend against pathogens in the intestine.
L) Mesangial cells
- These cells are found in the glomerulus of the nephron in between the capillary loop.
- They help to remove trapped residues to keep the filter free of clogging.
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge on Human Cells
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers.
How many cells are present in the human body?
By an estimate, there are 37 trillion cells in our body.
Are there any significant differences between animal and human cells?
How many chromosomes are in a human Somatic cell?
Somatic cells are normal body cells, and they have 46 chromosomes.
Are human cells prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Human cells are eukaryotic in nature. They have a well-defined nucleus.
So are cells free roaming in the lungs.? Can viruses attach to them in the lung then multiply.? I’ve seen videos that say you cannot CATCH a virus. The body gets rid of the viral load naturally when external forces, i.e., electromagnetic fields, are increased. Apparently, to get a virus, it needs to be injected into the body. Please explain.????????
Hi David, seems you are talking about alveolar macrophages which can roam in the airway tract to arrest foreign particles. These cells are meant to engulf viruses and other foreign particles and destroy them.
These macrophages can produce antibodies against virus particles which arrest them and help reduce viral load naturally. Hence, most viral infections including recent covid-19 are self-limiting in the body.
I am not sure of electromagnetic effects on viruses. But in general, these waves at specific frequencies can have an effect on the genetic component of cells including the virus.
Viruses can enter the body through the air (respiratory tract, blood I,e, by infection or another way of contact where body fluids can be involved.
Alveolar macrophages.
wow who knew learning about cells are complicated, but thanks anyway it's really helped in my homework and examination.
thanks for the info. appreciate it with gratitude. great work. God Bless
@Asiata Apineru Wright,thanks for stopping by. You are welcome.
its amazing thank you
Good one
it’s cool and all
thanks a bunch
helps.
like a lot!
thanks.
Thanks for giving such a great knowledge
very nice
It’s very nice, thanks alot.
Good 100% I Like It
Very good.
Yo man that was swag dude
wow all of it is bad
just kidding it worked good
it is nice
how about fibroblasts
At least it helps a lot in my research… Good one
It’s really very useful to me
Well done
An excellent work although I was not biological student but this work addicted me towards it and now lam a biology student
Useful information
Thanks
Helped lot
very educative indeed
i am a biological student and it helps me a lot in my research …great work …
thanks…..??
Very educative and understandable. I will visit it again. Thank you.
A good work.. it helped in my research.
kudos…… it’s quiet a good work.
Great
which cells in the human body synthesize collagen?
@Lisa M! Mostly by skin cells and connective tissue cells of bones, cartilage, eye cornea etc.
Helpful thx
okey guys thanks
I am a new teacher and this way of listing the cells and their functions is extremely helpful. Thank you!!
Helped me a lot
nice one
Great
thank you po because i know what are the clls in our body
this website really helped me do my assignment
nice!!!!!! it helped me in completing project
So helpful !!!!!
Thanks so much !!
nice concepts that we could understand easily the basic things
This was a really helpful website and it helped me a lot on what i needed to learn for when i grow up and become a student at McMaster and i hopefully can use these notes when im studying and one day ill become a surgen
Really cool for my daughter
@annie! Happy to have helped her..
Cool, helped me in science.
you are so right,even not only nice but fantastic
wonderful,,, i really liked this article so much.thanks
Really helpful. I LOVE IT!!!!!! but how do i copy and paste this
So thanks please help us more these one and I want to know more information
aki thanks much, it has realy helped me in cell cytology take away CAT. i wannah score everything
I wish it had hair Cells on here, but it looks like a good website. ?
What’s a sperm
Thank you so much the content realy helpd me alot
Very helpful,
Thank you so much!!!
Thank you ! it is very useful article and information to learn and teach about human body.
thanks you for this article
This was very very helpful thankyou and my friend Elissa helped too
great lesson for senior high
Sir , there are only 13 types of cells because blood cell is repeated in (alphabet f)
it don’t tells about all 14 types of cell in a human being it only tells us about a 8 cells
I love this it is wow !!!!!!!!! I hope it will help me in my exams
Short,interesting and very helpful.
Thanks so much.
Wonderful I loved it because It helped me in my holiday home work
It is very beautiful.Its help in my homework
oooh!I loved it .I am in std VII. It helped me in my project work. But I couldn’t copy it.
indeed its so important
Thanks, it was very helpful
WONDERFUL……. IT HELP ME A LOT
I want to know y males have RBCs more than female..???
And again this site is very useful for me and all….:) 🙂
@shyamnathani! RBC is needed to transport the oxygen from lungs to issues for generation of energy. Male body generates androgens (hormones) which triggers excess RBC formation. This excess RBC is required as male has more muscle mass and energy requirement than a female. Hence you can also notice that male hemoglobin level is 13-18 gm/dl while female HB level is 12-17 gm/dl. So in males not only RBC count but also HB level is high to meet the energy demands. And of-course male muscle mass is again due to andorgens.
this is very helpful, thank you very much but What types of cells protect us from infection and help repair cell damage?
@Asha! WBC cells help in fighting against infection. You can find more details here.
thx alot 2 who ever took their time to do this article now it may help me pass the 6th grade and not get held back
thanks for valuable information it helps a lot in my exams
tq
very helpful
Thanks a lot without you, I don,t know what will i have done now. you really helped me a lot
this is going to help me a lot now I will ace my project because I just used all of your information thanks again
i love science
I lyk it more….
thank you very much.
thanks.
It was nice and I like biology very mch
Extremely informative and helpful. I was required to create a project on cell size and function and this article helped me with almost every necessary requirement on the rubric. Thankyou!
We really enjoying contacting this site. Thank you!
This is very Helpful thanks
very concise simple language I love it
awesome
Helpeful just did my assignment am from Africa form 4 student
Very precise and simple words.love it
Some good info,also it helped me on my cells packet
hi guys
Very precise and informative. Thank you.
BALABALABOMBOM! you just gave me a pontastic idea, Lets go to OKIDO!!!!!!!!!
Thanks for ur information it helped me alot
TURNT UP SHAWTY
Gyftive
U r awesome thanks alot
its only 8
@apil joy! Please check it again. Remaining 6 types of cells are mentioned in alphabets a-f..
it relly helped me in my homework.thank you
..
Thanks a lot
Helpful! brilliant effort. I got much information
Thanks again.
Really helpful…………nice
Very useful information. Thanks.
Highly informative!!!:)
Thank you soo much this is very helpful
Absolutely awesome site! Explains all I need to know 😉 brilliant effort
very useful for completing my holiday homework.
very useful
very useful 🙂 🙂
This article helped in my projects too 🙂
This website helped me so much
this is great info
Thanks
Wanna copy paste it:(
wow
kashish!Sent you the copy by mail..:-)
Amazing
OMG this website helped me so much where did u get this great info?
Thank you by the way but, please answer my Question!!!
From regular teaching. Thanks for the compliment.
realy good website
i know! right?
@yolo!……:-)
10nxful it rili con3bot alot of hlp
really helpful, tanx.
Ekle Steve! welcome….
it helped me in studies by giving me useful knowledge about cell.
And by this i came first in my class.
Oh! congrats farhan….:-)
cool one but why cant i copy paste it?:/
I am a spazz kid. Thanks for the help.
Jarrod Starkey! you are welcome again..
hey spazz kid
thank u v much for this website this is v. Important for all student in the world”””’……
It saved me from failing in my exams
Help ful website helped me to pass my exams 😉
this site really helped me a lot and you know what i am in grade 10 and this was my holiday homework my tutor will be very happy when he sees this work ready for100% go alsie…………
thank you for this great website it helped me with my homework when nobody could
thanks it was realy helpful but you left oout a few… 🙁 :!
really luV dis article…it did helped me….its awesome!!
It is really helpful.
thx a lot of help from this web page awesome !!!!!!! :}
Hi my name is ashleigh i am yr 7 last term i learnt about cells
Just to clarify that you now you left out a few
Like egg cell
But by that it has helped with homework 😀 thanks ♡
awesome i thankful and it is very important for me to write notes thank u very much Studyread
Thanks helped in my biology assignment rili appreciate it
It is wonderful
Because that thing amazing in the science
It helped me a lot in completing my holiday homework 🙂
But why I was not able to copy this…..:(
Hi Abhishek! To prevent duplicate content on the net by other sites who just copy paste.
okay…………….anyway it helped me a lot………….;)
tbh I don’t think you know what your talking about
nice
also cool
really helpful!!!!
y can’t i copy the article?
THANKS A LOT FOR MY HELP .YOU KNOW WHAT THIS WEBSITE HELPED ME A LOT IN COMPLITING MY HOLIDAY HOME WORK (LONDON)
It helped me complete my school project
Thank you very much to the one who wrote this article i really learn alot from it…
you guys are actually right it really helps. I’m 12 and want to be a doctor so need all these information to learn. Thank you for who ever wrote this amazing article. 😉 🙂
Knowledgeful.
thanks it helped me alot
why i can’t copy this article to make it my personal notes 🙁
anyway thanks a lot, very helpful 🙂
I was able to copy just fine.
this stuff really works. thank u
awesome helped me a lot!!!
Browine, you are welcome again..
Thank you!!! this was so helpful!
It helped me on my paper