Chromosomes are DNA molecules containing part or whole genome of an organism.
They are present in the nucleus of the cell.
Chromosomes mostly have two bands separated by a centromere.
One can differentiate types of chromosomes based on their morphology, function and other differences.
Types of chromosomes
Based on the position of the centromere, chromosomes can be classified by morphological differences as
- Telocentric
- Acrocentric
- Sub-metacentric (L-shaped)
- Metacentric (V-shaped)
All four types of chromosomes can be found in eukaryotic cells
Teleocentric is like the letter “i” shapes and has a centromere at the terminal of the chromosome.
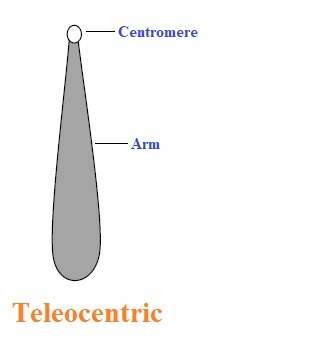
These chromosomes can be found extensively in the rodents like mice roaming in homes. These are absent in humans.
Acrocentric chromosomes: Here, one arm is very short and hard to observe.
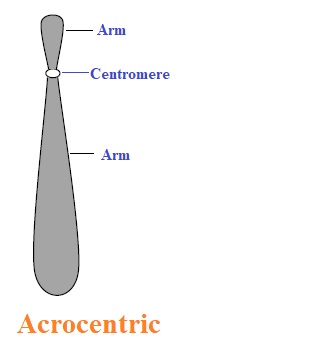
These chromosomes are found in humans as chromosome numbers 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22. Even this chromosome is found in domestic horses.
Sub-metacentric chromosomes: These chromosomes have unequal-length arms.
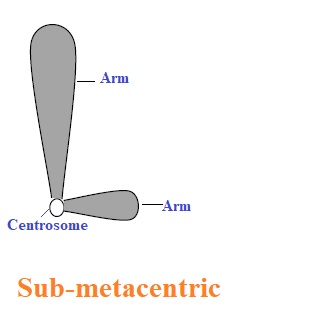
By shape, they are called L-shaped chromosomes.
Metacentric Chromosome: These chromosomes have two arms of equal length on either side of the centromere.
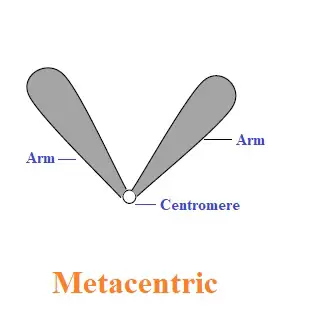
Their shape resembles the alphabet “V.” These metacentric chromosomes are found in humans as chromosomes 1, 3, 16, 19, and 20.
Halocentric chromosome: In these chromosomes, the entire length of acts as a centromere.
The chromosomes are classified into different types based on the shape and position of the centromere. According to the position of the centromere,
Types of chromosomes based on function
There are two basic types based on function as
- Autosome

- Sex chromosomes.
Autosomes: These are the chromosomes that control the somatic characteristics of the organism. There are 44 autosomes in humans.
Sex chromosomes: These chromosomes are two in number. They are involved in the determination of the sex of an organism. In humans, the male has one X and one Y chromosome as XY, and in females, there are two X chromosomes denoted as XX.
Other chromosomes:
B-chromosomes: These are supernumerary chromosomes and are present in addition to regular chromosomes. They tend to reduce the viability. They are present in plants like maize.
Double minutes: These are unstable chromosomes having no centromere and telomeres. They are found in cancer cells and show resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
