Blood cells are part of liquid connective tissue.
These cells are freely moving and have an essential function in the body.
As you might have known, there are 3 types of cells in the blood like
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
- Platelets.
Of the three, red blood cells and white blood cells carry important critical functions in the body.
The number of cells of these types is also relatively high.
Red Vs. White blood cell differences
Red blood cells are also called corpuscles because of their shape. Further, typical body cells lack a nucleus and other cell organelles.
White blood cells are typical animal cells with all the regular cell organelles.
The key differences among red blood cells vs. white blood cells relate to
- Functions
- Structures
- Numbers or concentrations in blood
- Life span
- Types
- Diseases
1. Functional differences
Red blood cells are involved in the distribution of oxygen. They transport oxygen from the lungs to all the tissues and cells of the body.
Further, they also help to carry carbon dioxide from tissues and cells back to the lungs.
Thus, red blood cells are involved in gaseous exchange in the body. Enzyme acetylcholinesterase is present on the membranes of RBC.
White blood cells have a different role in the body.
They help in protecting the body from infections and also assist in body repair.
They act as a body defense system and keep it healthy. They recognize the foreign cells and destroy them.
They produce antibodies against the foreign antigens and neutralize them.
Further, the neutrophils and macrophages eat and kill the harmful microorganisms in the blood and tissues.
Lysosomal enzymes are present in the WBC cells, which help autophagy and foreign cell destruction.
2. Anatomical and Structural differences
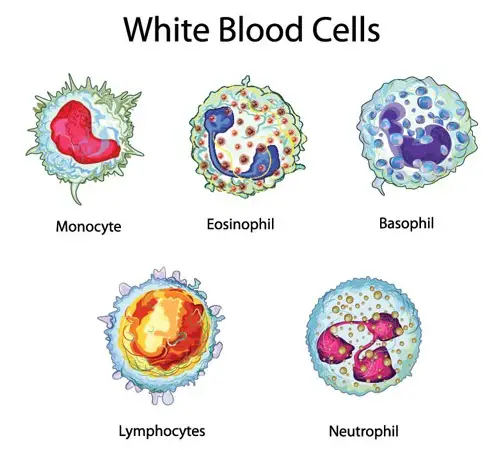
Red cells are disc-shaped with biconcave surfaces. At the same time, white cells are polymorphic (multi-shaped).
Further, red cells lack a nucleus, while white cells are multi-nucleated. Red cells are tiny in size, while white cells are large.
3. Numbers or concentration in blood
Red cells are pretty very high in concentration or number. Due to their high concentration, the blood is red.
White cells are comparatively low in number.
But, when their level increases in blood cancer, the condition is called leukemia (Leuk = white; aemia_ blood).
4. Life Span
RBCs have a lifespan of 120 days, while WBCs have a varying lifespan of around 3 to 20 days or sometimes years.
5. Types and variations among the cells
Red cells are of only one particular type.
Whereas the white blood cells are of 5 types:
- acidophils
- basophils
- neutrophils
- lymphocytes and
- monocytes.
6. Diseases and disorders
Both red and white cells can be the cause of diseases. A decrease in red cells is called anemia. At the same time, there is no effect of an increase in red cell count.
On the other hand, white cells have a disorder with both increased and decreased cell count.
An increase in white cells is termed leukemia, while their decrease is termed leukocytopenia or leukopenia.
Red Vs. White blood cells Similarities
The similarities of these cells are like
- Site of Production
- Mode of physiology
- Disease condition
1. Site of Production
The hemopoietic stem cells produce RBC and WBC inside the bone marrow.

So, their source and site of production are the same.
2. Mode of physiology
RBCs and WBCs are constantly in motion as they are part of blood, a liquid connective tissue.
So, these cells function by being in motion always.
3. In disease conditions
When there is malnutrition, both RBC and WBC count can be low due to decreased formation.
what are the similarities?
Hi, thanks for stopping by. The similarities are updated too. Please check again.
Thank you so much for writing this! It helped me so much in my assignments and it was very accurate, concise and coherent.